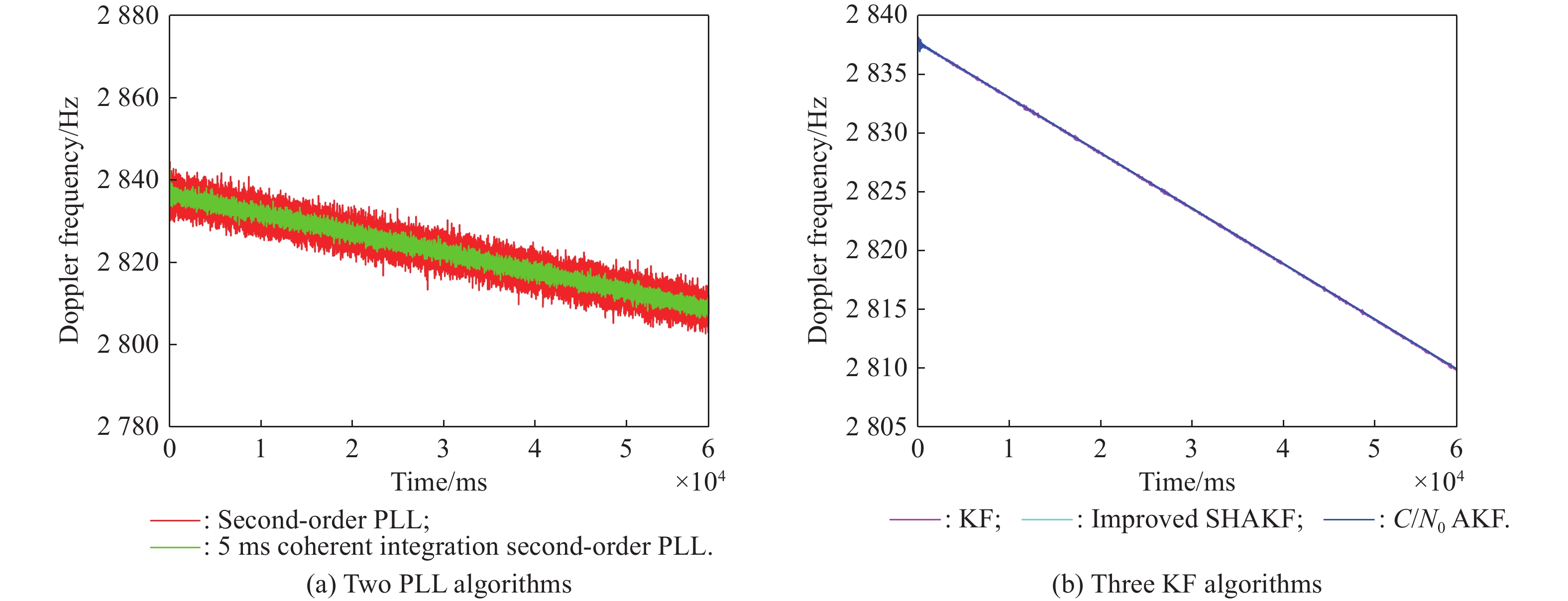
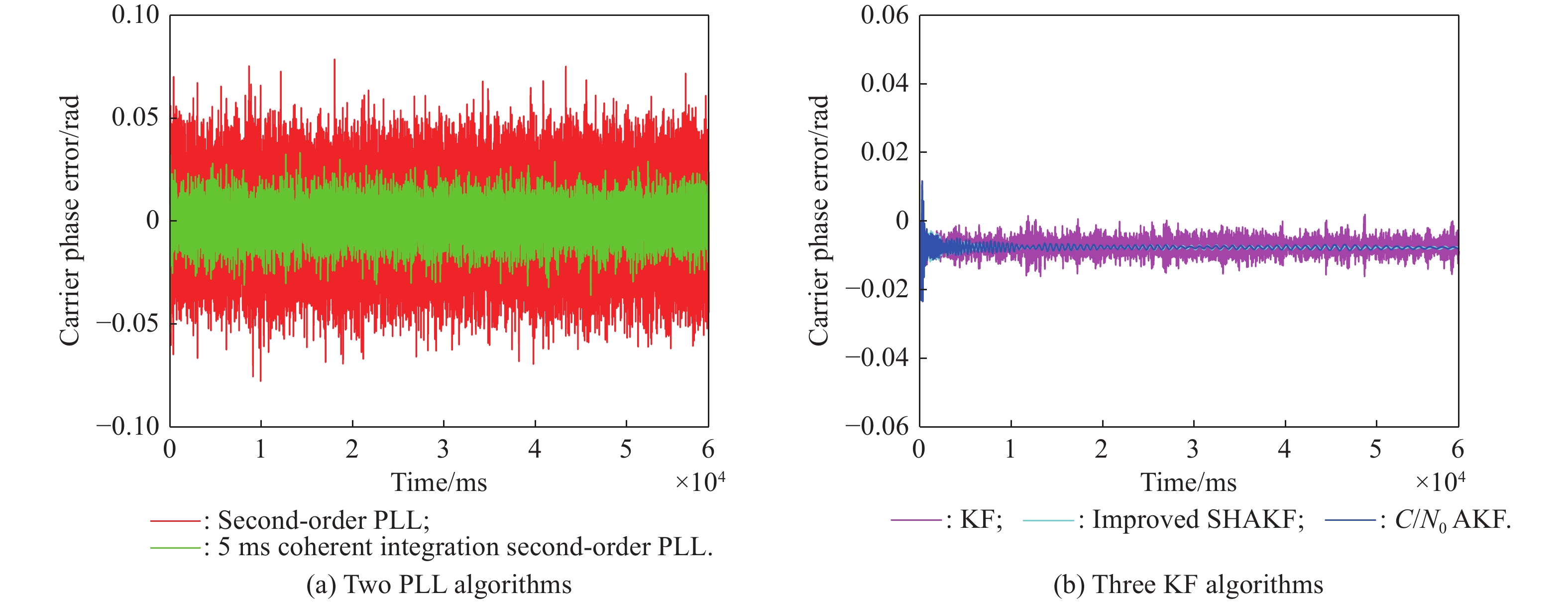
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 880-891.doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2025.000061
• • 上一篇
-
收稿日期:2023-09-18接受日期:2024-07-30出版日期:2025-08-18发布日期:2025-09-04
A tracking algorithm based on adaptive Kalman filter with carrier-to-noise ratio estimation under solar radio bursts interference
Xuefen ZHU1,*( ), Ang LI1(
), Ang LI1( ), Yimei LUO1(
), Yimei LUO1( ), Mengying LIN1(
), Mengying LIN1( ), Gangyi TU2(
), Gangyi TU2( )
)
- 1 School of Instrument Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2023-09-18Accepted:2024-07-30Online:2025-08-18Published:2025-09-04 -
Contact:Xuefen ZHU E-mail:zhuxuefen@seu.edu.cn;angli@seu.edu.cn;luoyimei19970316@163.com;linmengying@seu.edu.cn;tugangyi@nuist.enu.cn -
About author:
ZHU Xuefen was born in 1983. She received her B.S. degree in instrument science and optoelectronic engineering from Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, in 2004, and Ph.D. degree in navigation, guidance and control engineering from Southeast University, Nanjing, China, in 2010, respectively. She was a visiting Ph.D. student at the Navigation Signal Analysis and Simulation (NAVSAS) Group, Istituto Superiore Mario Boella (ISMB), Turin, Italy, from September 2007 to May 2009. She was a visiting scholar in the Department of Aerospace Engineering Science, University of Colorado, Boulder in the United States from October 2015 to October 2016. She is a professor in the School of Instrument Science and Engineering, Southeast University, China. Her research interests include global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signal processing and GNSS/inertial navigation system (INS) integration technologies. E-mail: zhuxuefen@seu.edu.cn
LI Ang was born in 1999. He received his B.S. degree in instrument science and optoelectronic engineering from Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, in 2022. He is currently working toward his Eng.D. degree in electronic and information engineering from Southeast University, Nanjing, China. His research focuses on global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers and prediction of total electron concentration in the ionosphere. E-mail: angli@seu.edu.cn
LUO Yimei was born in 1997. She received her B.S. degree in technique and instrumentation of measurements from China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, in 2019, and M.S. degree in measurement technology and instrument from Southeast University, Nanjing, China, in 2021. Her research focuses on solar radio bursts detection. E-mail: luoyimei19970316@163.com
LIN Mengying was born in 1994. She received her B.S. degree in electrical engineering and automation from Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan, China, in 2017, and Ph.D. degree in measurement technology and instrument from Southeast University, Nanjing, China, in 2023. Her research focuses on ionospheric modeling and predicting. E-mail: linmengying@seu.edu.cn
TU Gangyi was born in 1981. He received his B.S. degree in instrument science and optoelectronic engineering from Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, in 2004, and Ph.D. degree in measurement technology and instrument from Southeast University, Nanjing, China, in 2010. He was an associate director of the Institute of China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation from 2016 to 2020. He has been a professor in the School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, since 2021. His researches focus on external emitter radar system, electronic warfare system simulation, intelligent collaborative detection, software radio, and embedded system design. E-mail: tugangyi@nuist.enu.cn -
Supported by:This work was supported by the Foundation of Key Laboratory of Micro-inertial Instrument and Advanced Navigation Technology, Ministry of Education, China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61873064).
引用本文
. [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 36(4): 880-891.
Xuefen ZHU, Ang LI, Yimei LUO, Mengying LIN, Gangyi TU. A tracking algorithm based on adaptive Kalman filter with carrier-to-noise ratio estimation under solar radio bursts interference[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 36(4): 880-891.
"
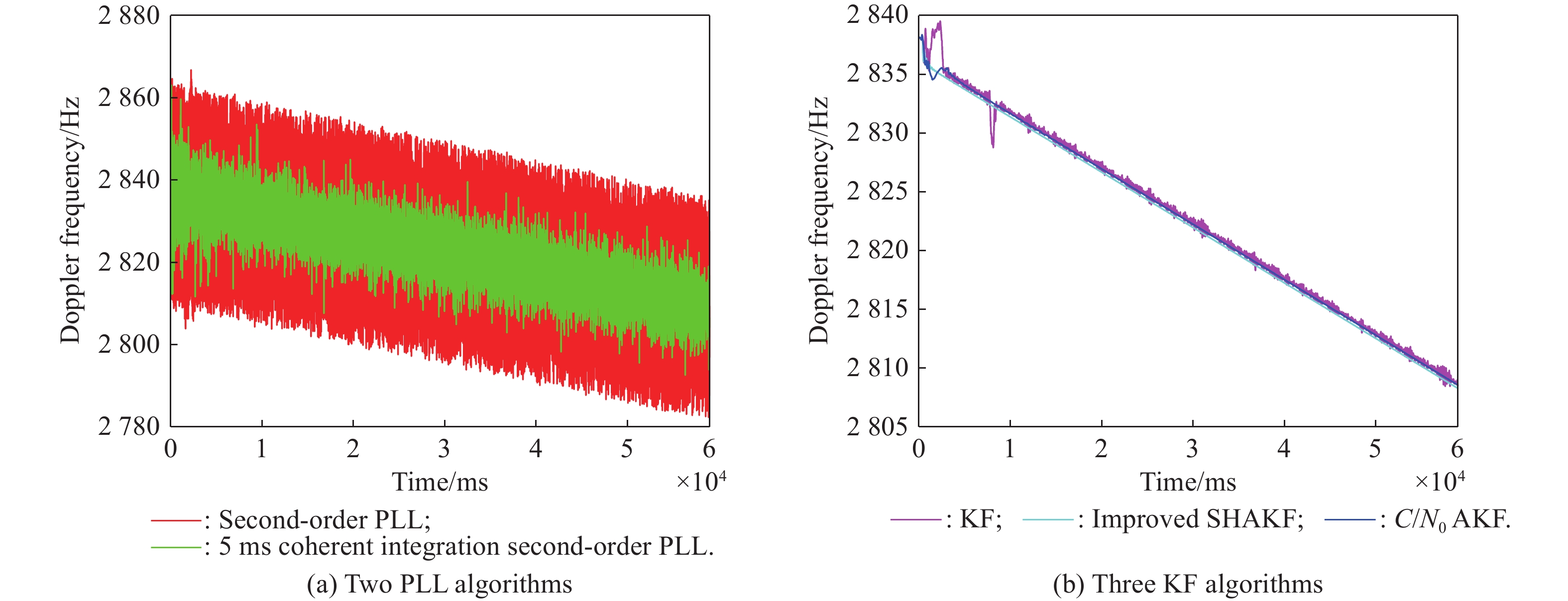
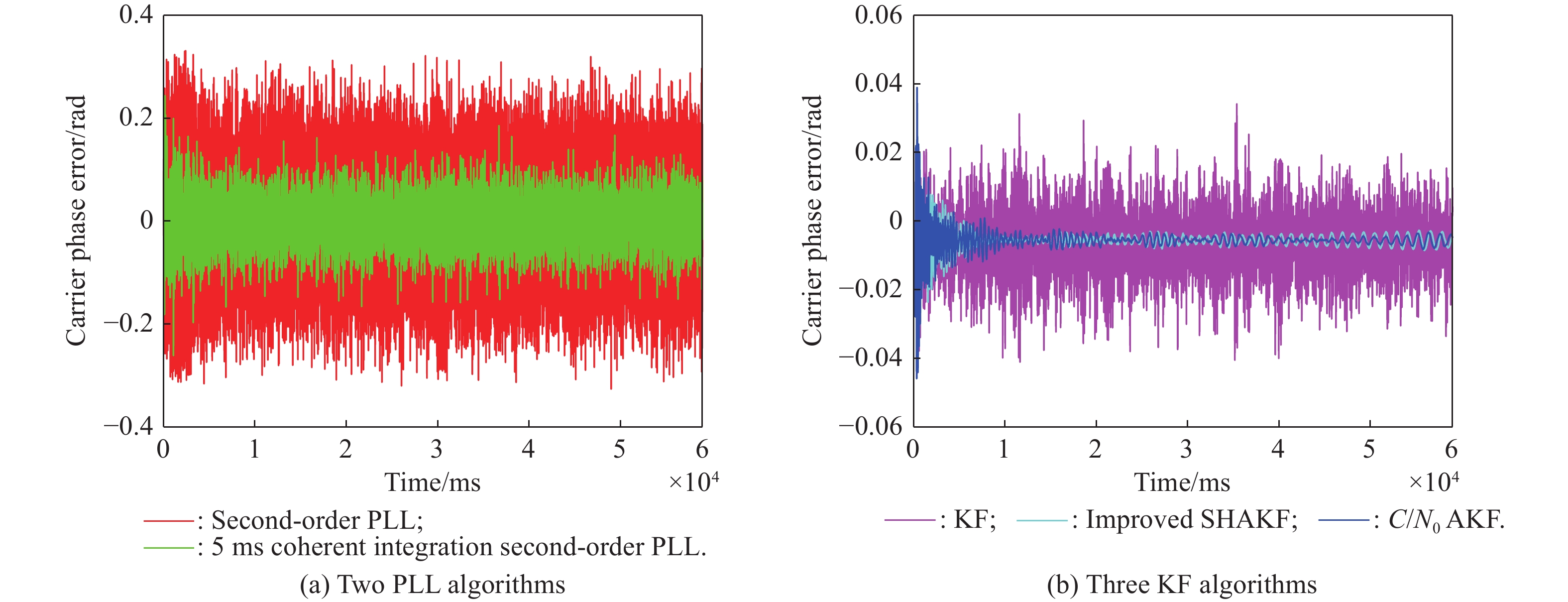
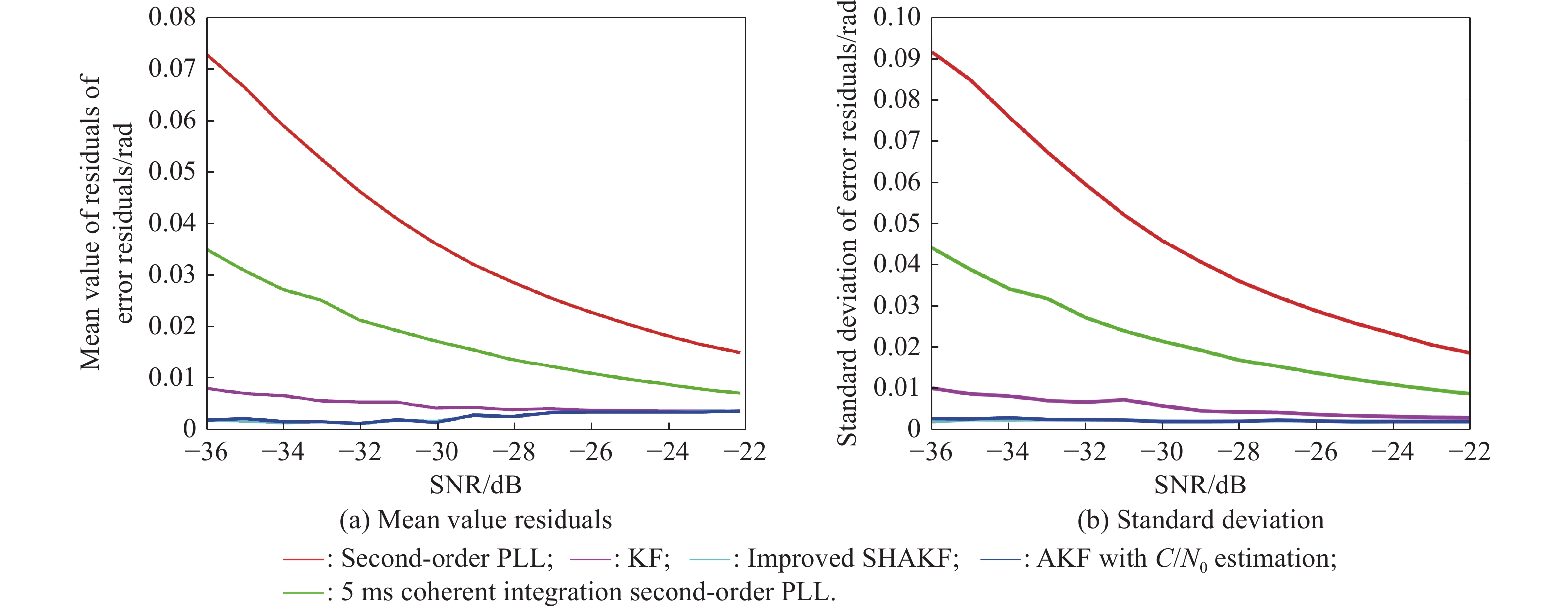
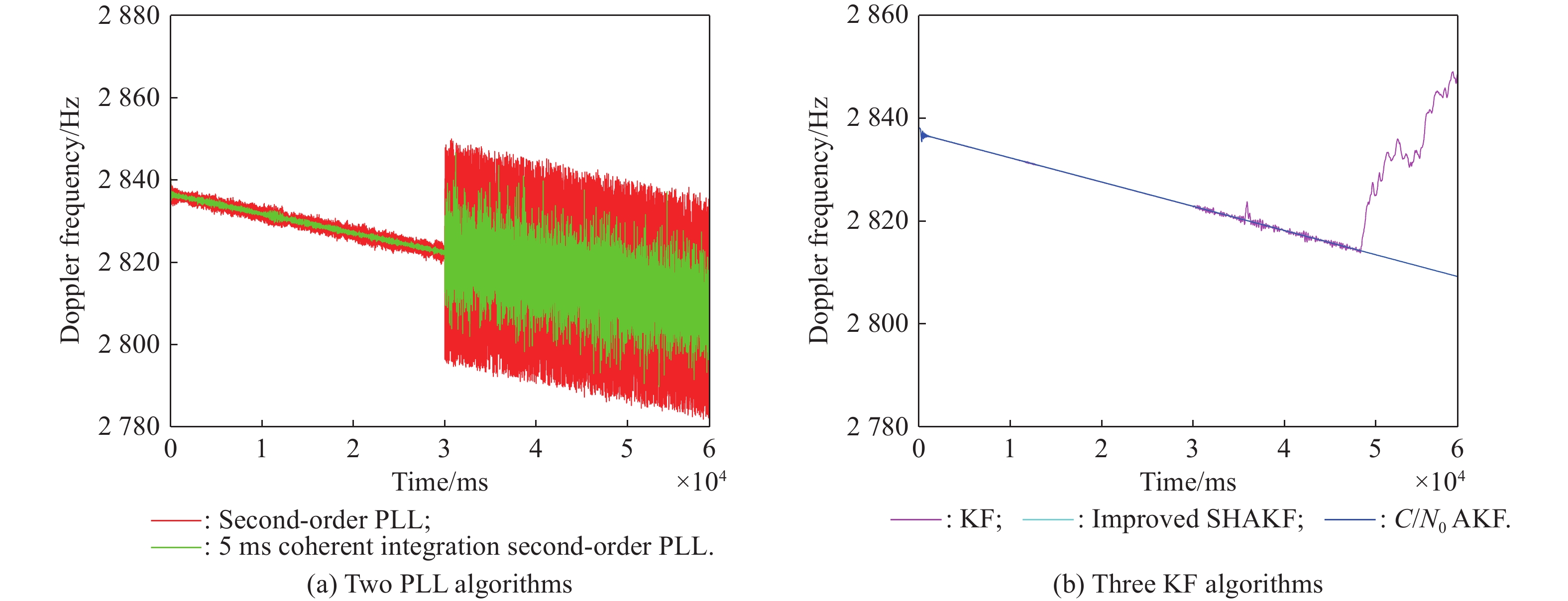
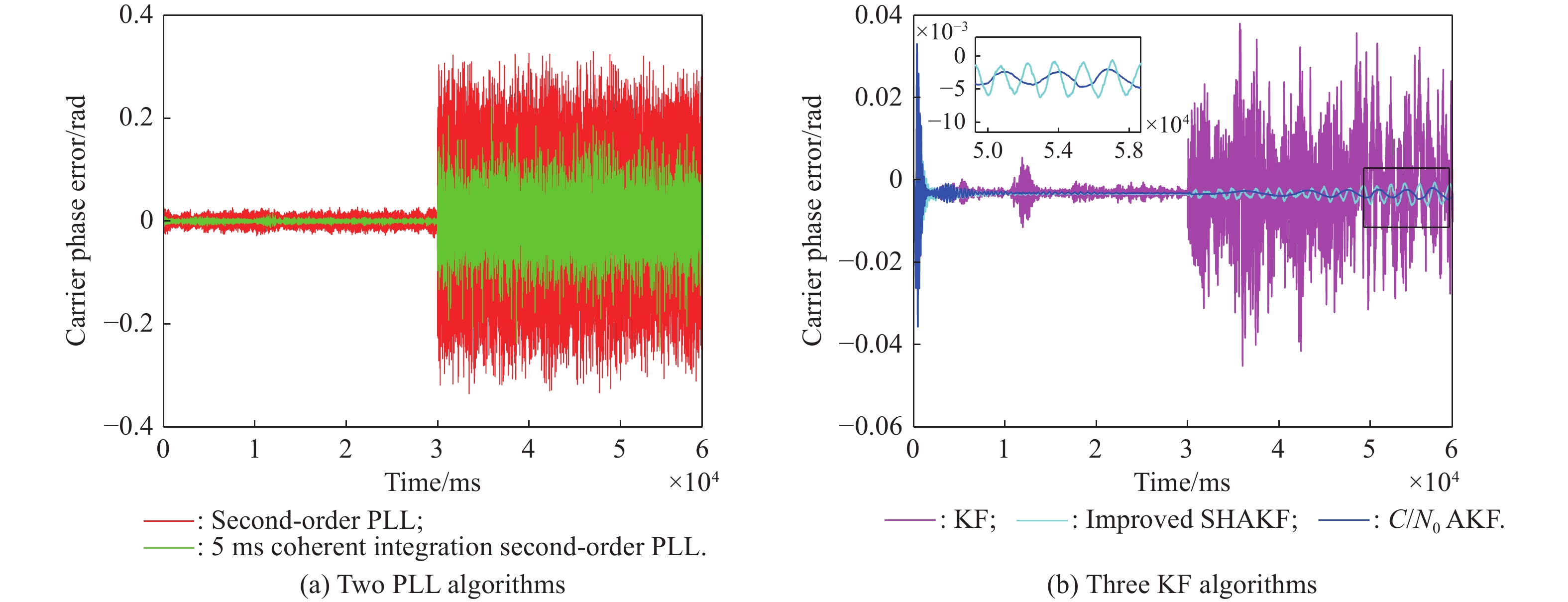
| Error type | Statistics | First stage of the third scene | Second stage of the third scene |
| Residual mean | Second-order PLL | ||
| 5 ms coherent integration second-order PLL | |||
| KF | |||
| Improved SHAKF | |||
| AKF with | |||
| Standard deviation | Second-order PLL | ||
| 5 ms coherent integration second-order PLL | |||
| KF | |||
| Improved SHAKF | |||
| AKF with |
| 1 |
ZENG H C, DENG J D, WANG P W A spawning particle filter for defocused moving target detection in GNSS-based passive radar. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 34 (5): 1085- 1100.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000033 |
| 2 |
NG Y, GAO G X GNSS multireceiver vector tracking. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53 (5): 2583- 2593.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2705338 |
| 3 | BILGEN B, INAL C. An open-source software for geodetic deformation analysis in GNSS networks. Earth Science Informatics, 2022, 15(3): 2051−2062. |
| 4 |
TRANQUILLA J Digital baseband processor for the GPS receiver modeling and simulations. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29 (4): 1343- 1349.
doi: 10.1109/7.259538 |
| 5 | JIN L, LV P, CUI X W, et al. Adaptive Kalman tracking algorithm for new generation GNSS signals. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2012, 52(9): 1249−1254, 1259. (in Chinese) |
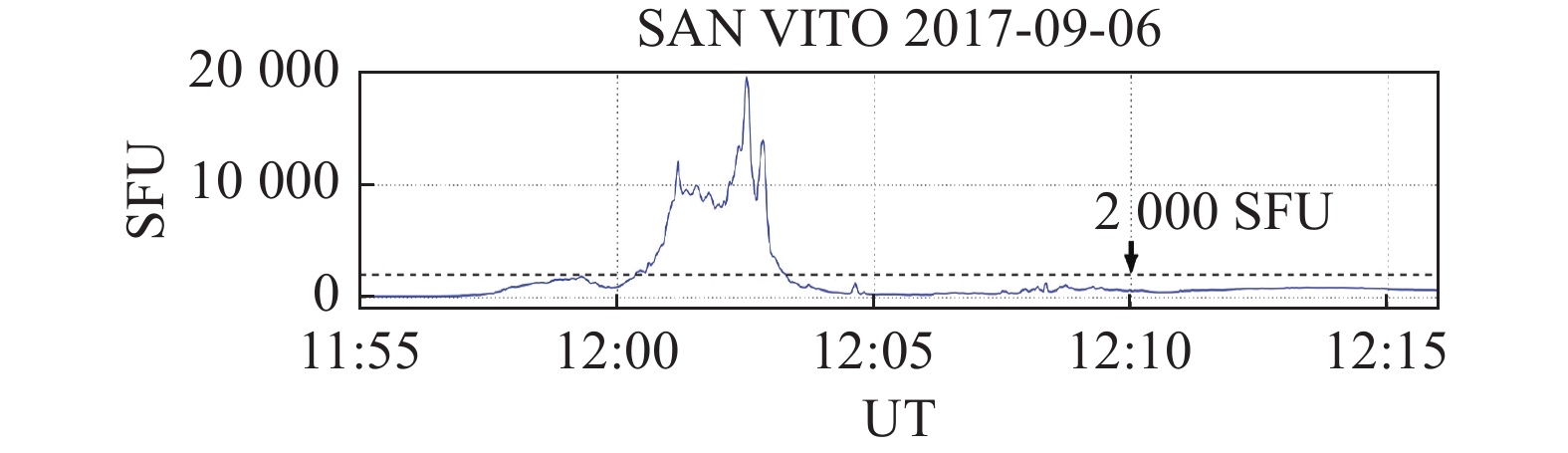
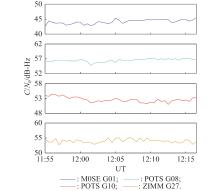
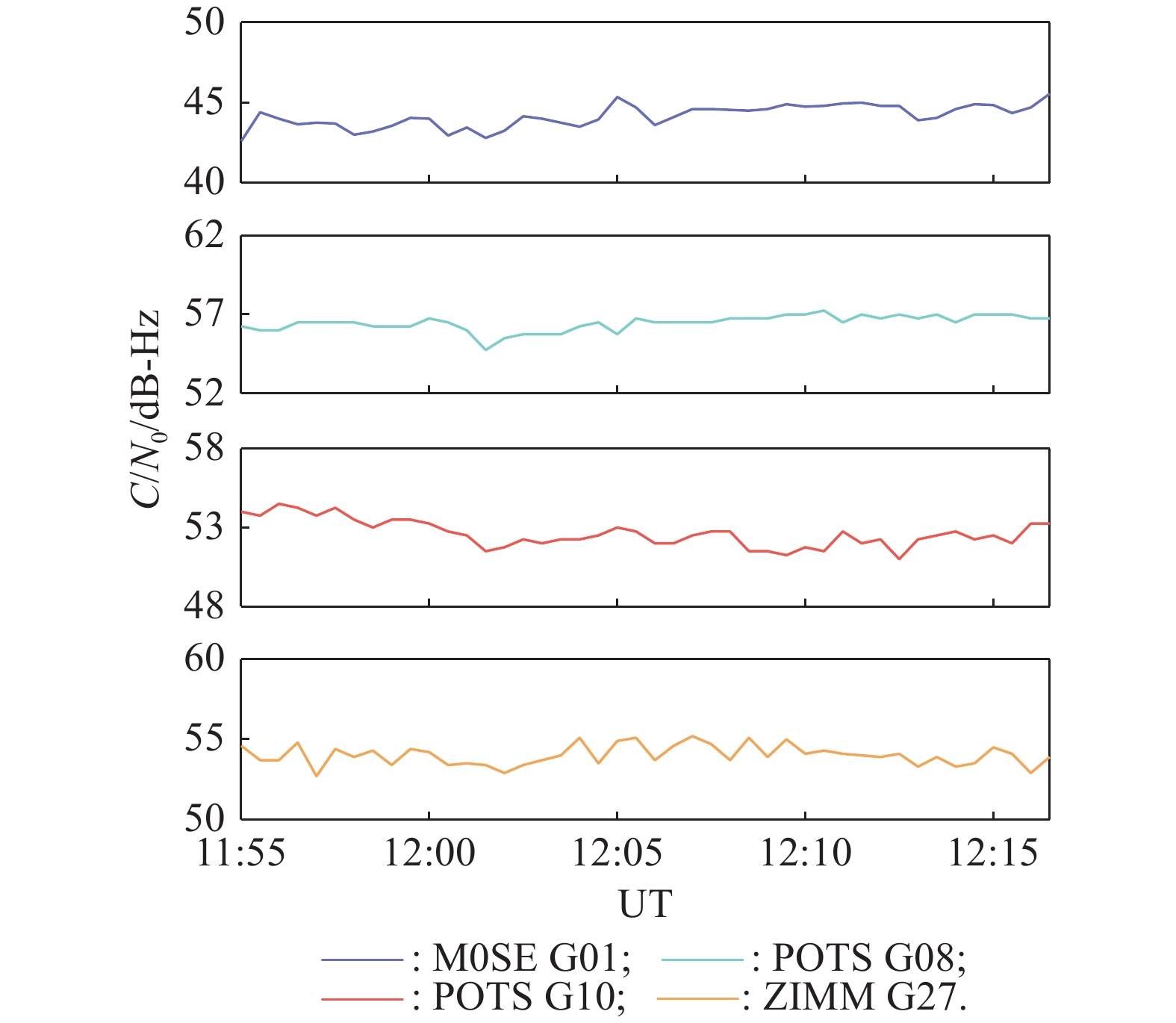
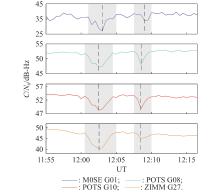
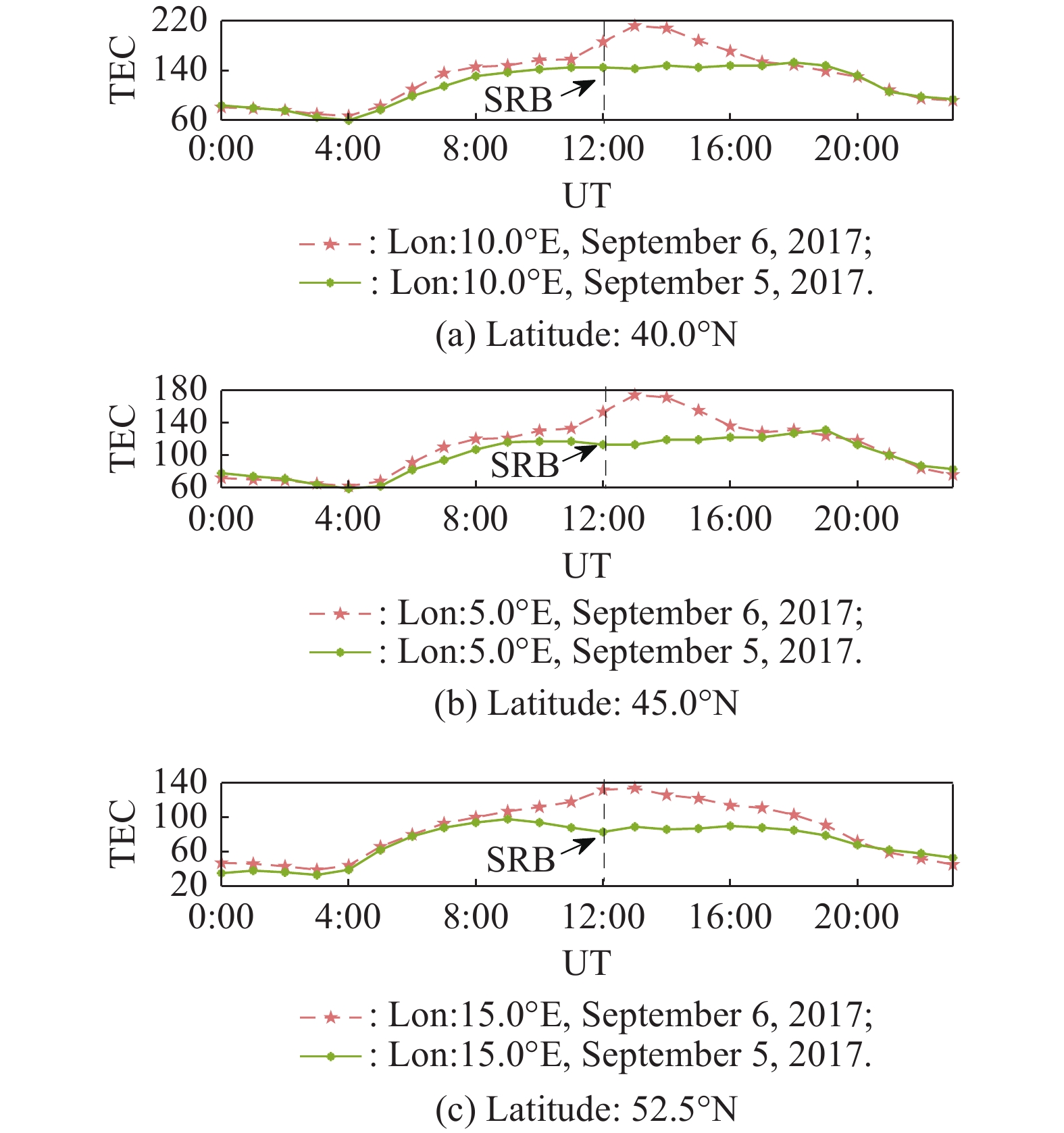
| 6 | DE PAULA E R, MARTINON A R F, CARRANO C, et al. Solar flare and radio burst effects on GNSS signals and the ionosphere during September 2017. Radio Science, 2022, 57(10): 1−15. |
| 7 | MCKEE S R, CILLIERS P J, LOTZ S, et al The effects of solar radio bursts on frequency bands utilised by the aviation industry in sub-Saharan Africa. Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate, 2023, 13 (1): 1- 11. |
| 8 |
KLOBUCHAR J A, KUNCHES J M, VANDIERENDONCK A J Eye on the ionosphere: potential solar radio burst effects on GPS signal to noise. GPS Solutions, 1999, 3 (2): 69- 71.
doi: 10.1007/PL00012794 |
| 9 |
SATO H, JAKOWSKI N, BERDERMANN J, et al Solar radio burst events on 6 September 2017 and its impact on GNSS signal frequencies. Space Weather, 2019, 17 (6): 816- 826.
doi: 10.1029/2019SW002198 |
| 10 | BISWAS T, PAUL A Effects of the relative dynamics of ionospheric irregularities and GPS satellites on receiver tracking loop performance. Radio Science, 2023, 58 (10): 1- 16. |
| 11 | JING S, ZHAN X X, LIU B Y, et al. Weak and dynamic GNSS signal tracking strategies for flight missions in the space service volume. Sensors , 2016, 16(9): 1412. |
| 12 | SKONE S, LACHAPELLE G, YAO D, et al. Investigating the impact of ionospheric scintillation using a GPS software receiver. Proc. of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, 2005: 1126−1137. |
| 13 |
LEE J, MORTON Y T J, LEE J, et al Monitoring and mitigation of ionospheric anomalies for GNSS-Based safety critical systems: a review of up-to-date signal processing techniques. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34 (5): 96- 110.
doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2716406 |
| 14 | WARD P W. Performance comparisons between FLL, PLL and a novel FLL-assisted-PLL carrier tracking loop under RF interference conditions. Proc. of the 11th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, 1998: 783−795. |
| 15 |
CURRAN J T, LACHAPELLE G, MURPHY C C Improving the design of frequency lock loops for GNSS receivers. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48 (1): 850- 868.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6129674 |
| 16 |
ZHANG H Y, XU L P, JIAN Y, et al A 2-step GPS carrier tracking loop for urban vehicle applications. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28 (5): 817- 826.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.05.01 |
| 17 |
VILA-VALLS J, CLOSAS P, NAVARRO M, et al Are PLLs dead? A tutorial on Kalman filter-based techniques for digital carrier synchronization. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2017, 32 (7): 28- 45.
doi: 10.1109/MAES.2017.150260 |
| 18 | ZHANG Q L, XU W Q, ZHANG W W, et al Multi-hypothesis square-root cubature Kalman particle filter for speaker tracking in noisy and reverberant environments. IEEE/ACM Trans. on Audio Speech and Language Processing, 2020, 28, 1183- 1197. |
| 19 | SAGE A P, HUSA G W. Adaptive filtering with unknown prior statistics. Proc. of the Joint Automatic Control Conference, 1969: 760−769. |
| 20 | ZHENG Z, LIU S R, ZHANG B T. An improved Sage-Husa adaptive filtering algorithm. Proc. of the 31st Chinese Control Conference, 2012: 5113–5117. |
| 21 | ZHAI H Q, WANG L H. A SINS/CNS/GPS online calibration method based on improved Sage-Husa adaptive filtering algorithm. Proc. of the 8th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications, 2022: 159–164. |
| 22 | HUANG W G, ERCHA A, SHEN H, et al Impact of intense L-band solar radio burst on GNSS performance and positioning accuracy. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2018, 33 (1): 1- 7. |
| 23 | KINTNER P M, O’HANLON B, GARY D E, et al Global positioning system and solar radio burst forensics. Radio Science, 2009, 44 (1): 1- 6. |
| 24 | CHAURASIYA S K, PATEL K, SINGH A K. Total electron content forecasting with neural networks during intense geomagnetic storms of the solar maximum and moderate years of solar cycle 24 in the low latitude Indian region. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2018, 368(9): 79. |
| 25 | DING X Y, WANG Q Design of carrier tracking loop based on adaptive strong tracking Sage-Husa Kalman filter. Electronics Optics & Control, 2019, 26 (10): 12- 16. |
| 26 | BALA B, LANZEROTTI L J, GARY D E, et al Noise in wireless systems produced by solar radio bursts. Radio Science, 2002, 37 (2): 1- 7. |
| 27 |
JIANG C, WANG S L, WU B, et al A state-of-charge estimation method of the power lithium-ion battery in complex conditions based on adaptive square root extended Kalman filter. Energy, 2021, 219, 119603.
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.119603 |
| 28 | QIAO S H, FAN Y S, WANG G F, et al. Radar target tracking for unmanned surface vehicle based on square root Sage-Husa adaptive robust Kalman filter. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 2924. |
| 29 | HUANG H Q, WU H, ZHANG S, et al An improved Sage-Husa adaptive Kalman filtering applied to cooperative navigation of autonomous underwater vehicles. Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 570- 575. |
| 30 |
GUO Y J, YANG D Q, CHEN Z Z Object tracking on satellite videos: a correlation filter-based tracking method with trajectory correction by Kalman filter. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12 (9): 3538- 3551.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2933488 |
| 31 |
WANG Q, SHANG F, DU L M, et al Influence of B1 code correlation loop for vector tracking structures under complicated environment. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30 (6): 1053- 1063.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.06.01 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||