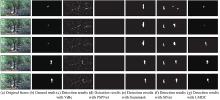
| 1 |
CAO J, CHOLAKKAL H, RAO A, et al D2Det: towards high quality object detection and instance segmentation. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, 11482- 11491.
|
| 2 |
LIU S T, JIANG K H, LIU Z X. Ship target detection of aerial reconnaissance image based on region covariance and objectness. Systems Engineering and Electronics. 2019, 41(5): 972–980. (in Chinese)
|
| 3 |
YANG J Y, SHI W, YUE H J, et al. Spatiotemporally scalable matrix recovery for background modeling and moving object detection. Signal Processing, 2019, 168: 107362.
|
| 4 |
MERILAITA S, SCOTT-SAMUEL N E, CUTHILL I C. How camouflage works. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2017, 372(1724): 20160341.
|
| 5 |
LI K J, LI Y B, ZHANG H R Evaluation of optical camouflage effect of air defense missile equipment. Laser & Infrared, 2019, 49 (5): 95- 100.
|
| 6 |
XU W D, WANG X W. Camouflage detection and evaluation theory and technology. Beijing: National Defense University Press, 2015.
|
| 7 |
CUI L Q, CHEN J J, REN Q Y, et al Saliency object detection based on multiple features and prior information. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25 (2): 321- 332.
|
| 8 |
OWENS A, BARNES C, FLINT A, et al Camouflaging an object from many viewpoints. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014, 2782- 2789.
|
| 9 |
WANG Z, YAN Y H, JIAO X Y Multi-index comprehensive evaluation of camouflage based on gray theory. ACTA Armamentarii, 2013, 34 (10): 1250- 1257.
|
| 10 |
LIU J J, HOU Q, CHENG M M, et al A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, 3912- 3921.
|
| 11 |
ZHAO J X, LIU J J, FAN D P, et al Egnet: edge guidance network for salient object detection. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019, 8778- 8787.
|
| 12 |
WANG B, MA Y J, LI P F Moving target detection based on improved three frame difference and background difference. Computer Systems & Applications, 2015, 24 (8): 154- 158.
|
| 13 |
BRUNYE T T, MARTIS S B, HORNER C, et al Visual salience and biological motion interact to determine camouflaged target detectability. Applied Ergonomics, 2018, 73, 1- 6.
doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2018.05.016
|
| 14 |
BRUNYE T T, MARTIS S B, KIREJCZYK J A, et al Camouflage pattern features interact with movement speed to determine human target detectability. Applied Ergonomics, 2019, 77, 50- 57.
doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2019.01.004
|
| 15 |
DAVIDSON M Perturbation approach to spatial brightness interaction in human vision. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1968, 58 (9): 1300- 1308.
doi: 10.1364/JOSA.58.001300
|
| 16 |
BARNICH O, DROOGENBROECK M V ViBE: a powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences. Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2009, 945- 948.
|
| 17 |
GONG W G, LIU R Y, ZHANG R Foreground segmentation under sudden illumination changes by feature fusion. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43 (12): 4164- 4169.
|
| 18 |
TAO H J, LU X B Smoke vehicle detection based on robust codebook model and robust volume local binary count patterns. Image and Vision Computing, 2019, 86, 17- 27.
doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2019.03.008
|
| 19 |
WU Z J, GAO X Efficient practical codebook-precoding MIMO scheme based on signal space diversity. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27 (1): 1- 9.
|
| 20 |
LI Y F, LEI L, SONG J X, et al Combination of local binary pattern operator with sample consensus model for moving objects detection. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2018, 92, 44- 52.
|
| 21 |
XIAO F, CUTHILL I C Background complexity and the detectability of camouflaged targets by birds and humans. Proc. of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2016, 283, 20161527.
|
| 22 |
CHEN D L, XU G L. Cross-domain person re-identification method based on attention mechanism to learn intra-domain variance. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1307.TP.20210705.0904.004. html.
|
| 23 |
ZHAN Y F, WANG C Y, WANG X G A simple baseline for multi-object tracking, computer vision and pattern recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129 (11): 3069- 3087.
doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01513-4
|
| 24 |
HAUNG H J, YANG W J, CHEN X T. EANet: enhancing alignment for cross-domain person re-identification. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.11369.
|
| 25 |
ZHAO H S, SHI J P, QI X J Pyramid scene parsing network. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, 6230- 6239.
|
| 26 |
TSAI Y H, YANG M H, BLACK M J Video segmentation via object flow. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, 3899- 3908.
|
| 27 |
NARKI N, PERAZZI F, WANG O, et al Bilateral space video segmentation. Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016, 743- 751.
|
| 28 |
WANG Q, ZHANG L, BERTINETTO L Fast online object tracking and segmentation: a unifying approach. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, 1328- 1338.
|
| 29 |
OH S W, LEE J Y, SUNKAVALLI K, et al Fast video object segmentation by reference-guided mask propagation. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, 7376- 7385.
|
| 30 |
FAN D P, JI G P, SUN G, et al Camouflaged object detection. Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, 2774- 2784.
|
| 31 |
MARGOLIN R, ZELNIKMANOR L, TAL A How to evaluate foreground maps? Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014, 248- 255.
|
 ), Chuntong LIU(
), Chuntong LIU( ), Hongcai LI(
), Hongcai LI( ), Zhongye LIU(
), Zhongye LIU( )
)