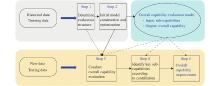
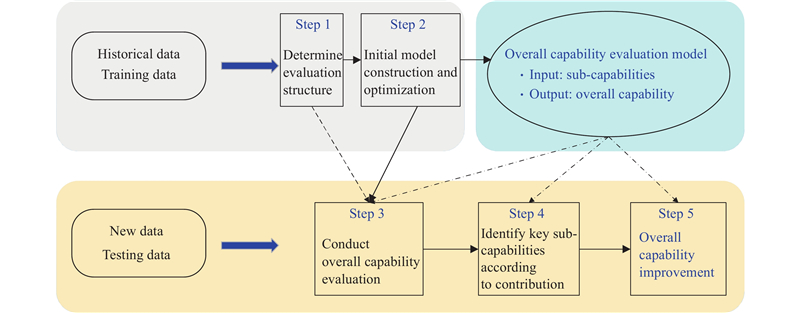
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 1231-1244.doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2024.000095
-
收稿日期:2022-12-26出版日期:2024-10-18发布日期:2024-11-06
Accountable capability improvement based on interpretable capability evaluation using belief rule base
Xuan LI1( ), Jiang JIANG1(
), Jiang JIANG1( ), Jianbin SUN1(
), Jianbin SUN1( ), Haiyue YU1(
), Haiyue YU1( ), Leilei CHANG1,2,*(
), Leilei CHANG1,2,*( )
)
- 1 College of Systems Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 China-Austria Belt and Road Joint Laboratory on Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Manufacturing, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
-
Received:2022-12-26Online:2024-10-18Published:2024-11-06 -
Contact:Leilei CHANG E-mail:xlhunan@126.com;jiangjiangnudt@163.com;sunjianbin@nudt.edu.cn;haiyue_nudt@163.com;leileichang@hotmail.com -
About author:
LI Xuan was born in 1982. She received her Ph.D. degree from National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, in 2017. She is an associate professor of the Big Data and Decision Lab in National University of Defense Technology. Her research interests include big data analysis, data engineering and application in the military background. E-mail: xlhunan@126.com
JIANG Jiang was born in 1980. He received his Ph.D. degree from National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, in 2011. He is an associate professor with National University of Defense Technology. His research interests include capability evaluation, risk assessment, and design of technology systems in the military background. E-mail: jiangjiangnudt@163.com
SUN Jianbin was born in 1989. He received his Ph.D. degree from National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, in 2018. He is an associate professor with National University of Defense Technology. His research interests include system of systems engineering management and decision analysis under uncertainty. E-mail: sunjianbin@nudt.edu.cn
YU Haiyue was born in 1991. He received his Ph.D. degree in management science and engineering from National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, in 2020. He is now a lecturer in management science and engineering with College of Systems Engineering at National University of Defense Technology. His main research interests include reliability modeling and evaluation of complex systems under uncertainty, testing, and evaluation of the intelligent system. E-mail: haiyue_nudt@163.com
CHANG Leilei was born in 1985. He received his Ph.D. degree from National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, in 2014. He is an associate professor with Hangzhou Dianzi University. He was a research fellow at Nanyang Technological University. His research interests include capability evaluation and improvement in the military background, and evaluation approaches in other theoretical and practical practices. E-mail: leileichang@hotmail.com -
Supported by:This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (72471067; 72431011; 72471238; 72231011; 62303474; 72301286), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang (GK239909299001-010).
引用本文
. [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(5): 1231-1244.
Xuan LI, Jiang JIANG, Jianbin SUN, Haiyue YU, Leilei CHANG. Accountable capability improvement based on interpretable capability evaluation using belief rule base[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(5): 1231-1244.
"
| Number | Sub-capability | Representative index | Type | Range |
| 1 | Surveillance (S) | Maximum surveillance distance/km | Benefit | [0, |
| 2 | Positioning (P) | Position precision coefficient/km | Cost | [0.1 4] |
| 3 | Identification (I) | Target identification belief level | Benefit | [0, 1] |
| 4 | Tracking (T) | Target track filtering precision | Cost | [0, 2.5] |
| 5 | Anti-jamming (AJ) | Disturbance suppression ration | Benefit | [0, 1] |
"
| Number | θ | IF (sub-capabilities) | THEN (overall capability)/% | Comment | |||||||
| S | P | I | T | AJ | High | Medium | Low | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | Least optimal condition | |
| 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | Optimal condition | ||
| 3 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 70 | 30 | 0 | Under influence | ||
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 0.3 | 2 | 0.4 | 40 | 40 | 20 | Under influence | ||
| 5 | 1 | 2000 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 50 | 30 | 20 | Under influence | |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 50 | 40 | 10 | Under influence | ||
"
| Scheme number | Key sub-capability | Overall capability/% | Cost | |||||
| Surveillance | Positioning | Identification | High | Medium | Low | |||
| 1 | 1.80 | 0.50 | 61.05 | 25.44 | 13.51 | 52 | ||
| 2 | 1.80 | 0.60 | 67.17 | 24.99 | 7.84 | 112 | ||
| 3 | 1.50 | 0.60 | 69.70 | 25.46 | 4.84 | 142 | ||
| 4 | 1.50 | 0.70 | 71.61 | 23.09 | 5.30 | 202 | ||
| 5 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 75.83 | 18.38 | 5.79 | 322 | ||
| 6 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 78.42 | 15.74 | 5.84 | 382 | ||
| 7 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 80.67 | 13.57 | 5.76 | 392 | ||
| 8 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 81.84 | 12.52 | 5.64 | 397 | ||
"
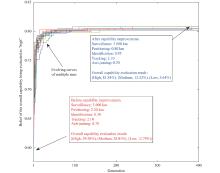
| Capability | Status of sub-capabilities | Overall capability (“high”)/% | Cost |
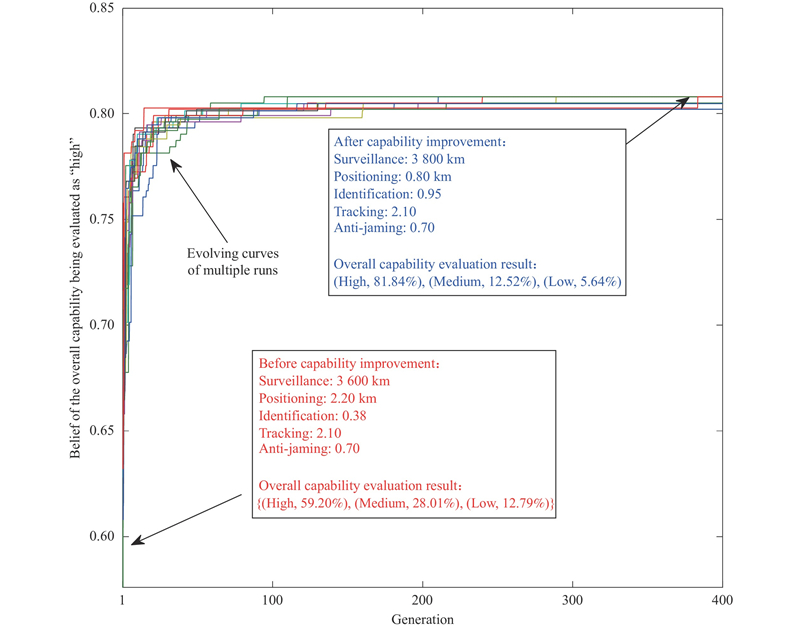
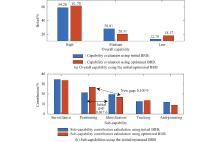
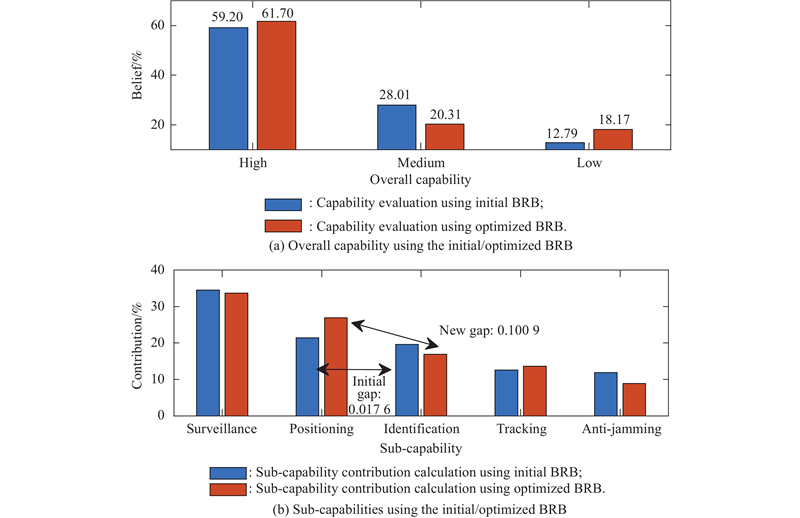
| Present capability (before capability improvement) | S=3 600 km; P=2.20 km; I=0.38; T=2.10; AJ=0.70 | 59.20 | NA |
| Overall capability improved by initial BRB | S=3 600 km; P=2.20 km; I=0.38; T=2.10; AJ=0.70 | 81.84 | 397 |
| Overall capability improved by optimized BRB | S=3 600 km; P=2.20 km; I=0.38; T=2.10 AJ=0.70 | 80.82 | 295 |
| S=3 600 km; P=2.20 km; I=0.38; T=2.10 AJ=0.70 | 81.34 | 370 |
"
| Approach | Parameter setting | MAE | Analytical step | Adoptable |
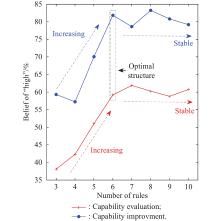
| Initial BRB | Six rules, three scales in the capability evaluation results. | 3.44e-03 | Yes | Yes |
| Optimized BRB | 6.25e-03 | |||
| BPNN | The number of layers is 2, the number of neurons is 10, the epoch is | 3.23e-03 | No | No |
| SVM | Kernal function is RBF, C=0.2 | 1.41e-02 | No | No |
| 1 | CORREIA J Military capabilities and the strategic planning conundrum. Security & Defence Quarterly, 2019, 24 (2): 21- 50. |
| 2 | SMEETS M The strategic promise of offensive cyber operations. Strategic Studies Quarterly, 2018, 12 (3): 90- 113. |
| 3 |
PIOTROWSKY L, JAESCHKE T, KUEPPERS S, et al Enabling high accuracy distance measurements with FMCW radar sensors. IEEE Trans. on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 67 (12): 5360- 5371.
doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2930504 |
| 4 | U. S. Department of Defense. FY 2022 Defense Budget. https://www.defense.gov/Spotlights/FY2022-Defense-Budget/. |
| 5 | LIU R X, WU L, XIE Z G, et al Auxiliary situation analysis for air defense system based on generative adversarial network. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44 (8): 2522- 2529. |
| 6 | QIAN L W, XU X Q, DOU Y J, et al System capability requirements recommendation method based on RIMER method. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44 (12): 3719- 3727. |
| 7 |
ZHAO L D, WANG B, HE J, et al SE-DEA-SVM evaluation method of ECM operational disposition scheme. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33 (3): 600- 611.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2022.000058 |
| 8 |
BLANKENSHIP B, LIN-GREENBERG E Trivial tripwires?: military capabilities and alliance reassurance. Security Studies, 2022, 31 (1): 92- 117.
doi: 10.1080/09636412.2022.2038662 |
| 9 |
WALLIS J, POWLES A Burden-sharing: the US, Australia and New Zealand alliances in the Pacific islands. International Affairs, 2021, 97 (4): 1045- 1065.
doi: 10.1093/ia/iiab081 |
| 10 |
JIANG J, CHANG L L, ZHANG L M, et al Retraceable and online multi-objective active optimal control using belief rule base. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 233, 107553.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107553 |
| 11 |
CHANG L L, JIANG J, SUN J B, et al Disjunctive belief rule base spreading for threat level assessment with heterogeneous, insufficient, and missing information. Information Sciences, 2019, 476, 106- 131.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.004 |
| 12 |
CHANG L L, FU C, WU Z J, et al A data-driven method using BRB with data reliability and expert knowledge for complex systems modeling. IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man, Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52 (11): 6729- 6743.
doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3095524 |
| 13 |
CHANG L L, ZHANG L M, FU C, et al Transparent digital twin for output control using the belief rule base. IEEE Trans. on Cybernetics, 2022, 52 (10): 10364- 10378.
doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3063285 |
| 14 |
KAUSHAL M, KHEHRA B S, SHARMA A Soft computing based object detection and tracking approaches: state-of-the-art survey. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 70, 423- 464.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.05.023 |
| 15 | WHITLEY D, RANA S, DZUBERA J, et al Evaluating evolutionary algorithms. Artificial Intelligence, 1996, 85 (1/2): 245- 276. |
| 16 | KRAMER O, KRAMER O. Genetic algorithms. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017. |
| 17 |
TANG M N, CHEN S J, ZHENG X H, et al Sensors deployment optimization in multi-dimensional space based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29 (5): 969- 982.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2018.05.09 |
| 18 |
WANG L S B, WANG X S, XU Z H Principle and approach to polarization modulation for radar super-resolution. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023, 53, 993- 1007.
doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141 |
| 19 |
AUBRY A, MAIO A D, ROSAMILIA M Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for N-LOS radar surveillance. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70 (10): 10735- 10749.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3102315 |
| 20 | U. S. Department of Defense. The DoDAF architecture framework version 2.02. https://dodcio.defense.gov/Library/DoD-Architecture-Framework/. |
| 21 |
ZENG L H, YAO F Q, ZHANG J Z, et al Dynamic spectrum access based on prior knowledge enabled reinforcement learning with double actions in complex electromagnetic environment. China Communications, 2022, 19 (7): 13- 24.
doi: 10.23919/JCC.2022.07.002 |
| 22 |
GUO S, AKHTAR S, MELLA A A method for radar model identification using time-domain transient signals. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57 (5): 3132- 3149.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3074129 |
| 23 |
YAN J K, JIAO H, PU W Q, et al Radar sensor network resource allocation for fused target tracking: a brief review. Information Fusion, 2022, 86/87, 104- 115.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.06.009 |
| 24 |
LI K, JIU B, PU W Q, et al Neural fictitious self-play for radar anti-jamming dynamic game with imperfect information. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58 (6): 5533- 5547.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3175186 |
| 25 |
DENG W, ZHANG X X, ZHOU Y Q, et al An enhanced fast non-dominated solution sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective problems. Information Sciences, 2022, 585, 441- 453.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.11.052 |
| 26 | DING D R, WANG Z D, HAN Q L, et al Neural-network-based output-feedback control under round-robin scheduling protocols. IEEE Trans. on Cybernetics, 2018, 49 (6): 2372- 2384. |
| 27 | OUCHEN S, STEINHART H, BENBOUZID M, et al Robust DPC-SVM control strategy for shunt active power filter based on H∞ regulators. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 117, 105699. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||